Hematology disorders such as those caused by key plasma protein deficiencies that impede blood clotting or, conversely, result in excessive clotting, can result in serious medical complications or even death. Leveraging our experience in plasma-based clotting factors, Grifols is focused on widening our indication reach to help a larger number of patients living with these disorders.
Fostamatinib for chronic immune thrombocytopenia (ITP)
In people with ITP, the immune system attacks and destroys the body's own blood platelets, cells which play an active role in blood clotting and healing. Fostamatinib is the first new treatment for people with ITP in decades. It prevents the pathologic destruction of platelets by inhibiting a signaling cascade mediated by spleen tyrosine kinase (SYK).
Learn more about our approved fostamatinib treatment for ITP here.
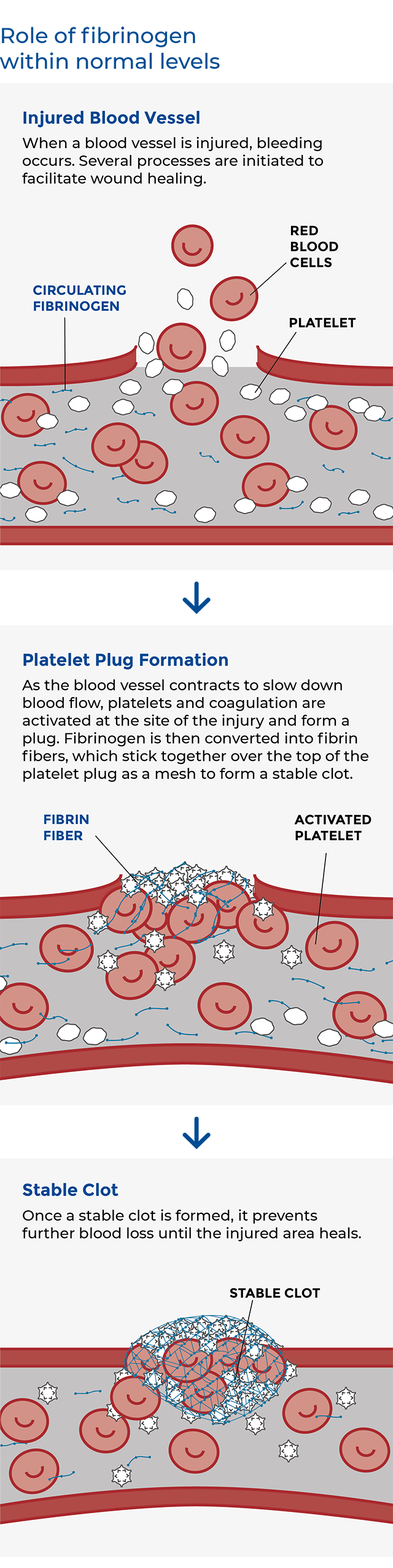
A fibrinogen for bleeding management
Fibrinogen is a blood plasma protein made in the liver that is involved in coagulation and wound healing. When the concentration of this protein in a person’s plasma falls below a critical level or when it does not function properly, the ability to stop the bleeding is compromised.
Grifols, through its Biotest group, has developed a new fibrinogen solution for the treatment of fibrinogen deficiency associated with severe blood loss. It is designed for greater convenience, faster preparation and room-temperature storage.
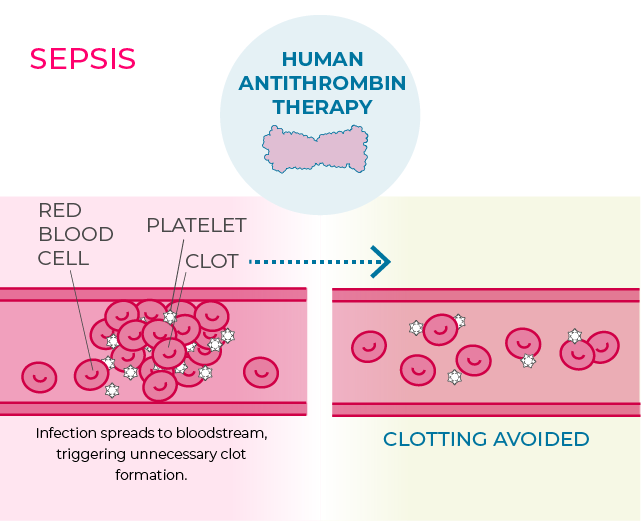
Antithrombin III (AT-III) and intensive care
Grifols continues advancing in AT-III to ensure the right coagulation balance for patients, and is investigating the potential of this protein in a clinical trial to treat a life-threatening coagulopathy that results from sepsis. In the U.S., roughly 60% of sepsis cases become severe,1 with 30 to 50%2 of these severe sepsis patients experiencing disseminated intravascular coagulopathy (DIC). DIC involves excessive clotting in the bloodstream that can lead to massive bleeding elsewhere in the body and can lead to multiorgan failure.
Antithrombin limits the blood’s ability to clot by inhibiting thrombin, an enzyme that presides over the conversion of a substance called fibrinogen to fibrin, which promotes blood clotting. Its balance in plasma is key to avoiding too much clotting or bleeding issues. Our AT-III is the only plasma-derived medicine authorized and approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat AT-III deficiency, an inherited blood-clotting disorder.
1 Angus DC, Linde-Zwirble WT, Lidicker J, Clermont G, Carcillo J, Pinsky MR. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit Care Med. 2001;29(7):1303-1310.
2 Costello RA, Nehring SM. Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; July 12, 2022.
Developing Treatments
Patients are at the center of our far-ranging scientific research to develop therapeutic solutions to some of the world’s most pressing healthcare challenges.